Introduction
In the intricate world of business finance, where every decision can ripple through your operations, understanding your business’s debt-to-income ratio is crucial. This simple yet powerful metric is often overlooked, yet it is vital in guiding you toward financial health or warning of potential pitfalls. In this article, we’ll go over the importance of debt-to-income ratios, how they impact your business, and the steps you can take to manage them effectively.
Why Debt-to-Income Ratios Matter for Your Business
Your business’s debt-to-income ratio is more than just a number—it’s a reflection of your company’s financial equilibrium. A well-balanced ratio indicates that your business is on a solid footing, with enough income to comfortably cover its debts. On the other hand, a skewed ratio could spell trouble, signaling that debt obligations may be overwhelming your revenue streams. Understanding this ratio allows you to navigate the complexities of business finance with greater confidence and foresight.
The Role of Debt-to-Income Ratios in Business Health
Debt-to-income ratios act as a thermometer for your business’s financial health. They offer insight into how much of your income is committed to debt repayment, helping you gauge whether your business is thriving or merely surviving. A healthy ratio suggests that your business can not only meet its current obligations but also has room for growth and investment. Conversely, an unhealthy ratio may indicate that debt is stifling your business’s potential, leading to cash flow problems and limiting your ability to take advantage of new opportunities.
What is a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Breaking Down the Basics: Debt vs. Income
At its core, a debt-to-income ratio compares your business’s total debt to its total income. It’s a straightforward calculation, yet it encapsulates the delicate balance between what your business owes and what it earns. Debt includes all the money your business has borrowed, such as loans, credit lines, and other financial obligations. Income, on the other hand, encompasses all revenue streams, from sales and services to any additional sources of earnings.
How to Calculate Your Business’s Debt-to-Income Ratio
Then, divide this total by your gross monthly income—this is also known as gross monthly earnings or gross monthly profits. Your gross monthly profits are what you get after subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your monthly revenue.
Keep in mind that your gross monthly earnings don’t factor in fixed charges or any taxes owed by you or your business. The result is your DTI ratio.
For example:
Gross monthly profits: $50,000
Total loan repayments: $10,500
DTI ratio: ($10,500 / $50,000) X 100 = 21%
Examples of Debt-to-Income Ratio Calculations
Imagine two businesses: Business A and Business B. Business A has a total debt of $50,000 and an annual income of $200,000. Their debt-to-income ratio would be 25%. Business B, on the other hand, has a total debt of $120,000 and an annual income of $300,000, giving them a debt-to-income ratio of 40%. Despite Business B having a higher income, their higher debt load results in a less favorable ratio, highlighting the importance of keeping debt in check relative to income.

The Importance of Debt-to-Income Ratios
Understanding the Financial Pulse of Your Business
Your debt-to-income ratio offers a snapshot of your business’s financial pulse, same to a doctor checking your vitals. It tells you how much of your revenue is tied up in debt repayment, giving you a clear picture of your financial flexibility. A low ratio indicates a healthy buffer, allowing your business to absorb shocks, invest in growth, and seize new opportunities. Conversely, a high ratio may signal that your business is operating on thin margins, where even a slight dip in income could jeopardize your ability to meet debt obligations.
How Lenders Use Debt-to-Income Ratios to Assess Risk
Lenders scrutinize your debt-to-income ratio to assess the risk of lending to your business. A lower ratio suggests that your business is financially stable and more likely to repay its debts, making you a more attractive candidate for loans. Conversely, a high ratio may raise red flags, indicating that your business might struggle to keep up with additional debt, which could lead to higher interest rates or even loan denial. Understanding this perspective can help you position your business more favorably when seeking financing.
The Impact of Debt-to-Income Ratios on Business Creditworthiness
Your debt-to-income ratio plays a crucial role in determining your business’s creditworthiness. A healthy ratio can enhance your business’s credit score, opening doors to better financing options and more favorable terms. On the flip side, a high ratio can drag down your credit score, limiting your access to credit and increasing the cost of borrowing. Maintaining a balanced ratio is essential for preserving your business’s financial reputation and ensuring that you have the resources needed to grow.
Types of Debt in Your Business
Short-Term vs. Long-Term Debt: What’s the Difference?
Understanding the nuances between short-term and long-term debt is essential for managing your debt-to-income ratio effectively. Short-term debt typically includes obligations that are due within a year, such as lines of credit, short-term loans, and accounts payable. These are often used to manage cash flow or fund immediate needs. Long-term debt, on the other hand, includes loans and bonds that extend beyond a year. While long-term debt can provide significant capital for expansion, it also requires careful management to ensure that it doesn’t tip your debt-to-income ratio into dangerous territory.
Secured vs. Unsecured Debt: Understanding the Risks
Secured debt is backed by collateral, such as property or equipment, which reduces the lender’s risk and often results in lower interest rates. Unsecured debt, lacking collateral, poses a higher risk for lenders and usually comes with higher interest rates. While secured debt can be more cost-effective, it also puts your assets on the line. Unsecured debt, while less risky in terms of asset loss, can quickly escalate your debt-to-income ratio if not managed carefully. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about the types of debt your business takes on.
The Role of Business Loans in Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Business loans are a common source of debt, and they can significantly impact your debt-to-income ratio. Whether you’re borrowing to expand operations, purchase equipment, or cover short-term expenses, the key is to ensure that the loan’s benefits outweigh its impact on your ratio. Consider how the loan will affect your ability to meet other financial obligations and whether it will enhance your income in a way that keeps your debt-to-income ratio in check.
Credit Lines and How They Affect Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Credit lines offer flexibility, allowing your business to borrow as needed up to a certain limit. While this can be a useful tool for managing cash flow, it’s important to monitor how much of your credit line is utilized, as it directly impacts your debt-to-income ratio. High credit utilization can inflate your ratio, making your business appear more leveraged than it actually is. Keeping credit line usage to a minimum, or paying down balances regularly, can help maintain a healthy ratio.
Income Streams and Their Impact
Analyzing Your Business’s Revenue Sources
To manage your debt-to-income ratio effectively, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of your revenue streams. Analyze where your income is coming from, whether it’s sales, services, or other sources. Understanding the diversity and reliability of these streams helps you gauge how stable your income is and how well it can support your debt obligations. A diversified income base can cushion your business against downturns in any single area, helping to maintain a favorable debt-to-income ratio.
Diversifying Income to Improve Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Diversification is a powerful strategy for improving your debt-to-income ratio. By expanding your revenue streams, you can increase your total income, which in turn lowers your ratio. This might involve exploring new markets, offering additional products or services, or tapping into new customer segments. The more varied and robust your income sources, the better positioned your business is to handle debt and maintain financial health.
Seasonal Income Fluctuations and Debt-to-Income Ratios
Seasonal fluctuations can complicate your debt-to-income ratio, especially if your business experiences significant variations in revenue throughout the year. For businesses with seasonal income, it’s important to plan for these fluctuations by building up reserves during peak periods to cover leaner times. This approach helps smooth out your income and ensures that your debt-to-income ratio remains stable, even when revenue dips.
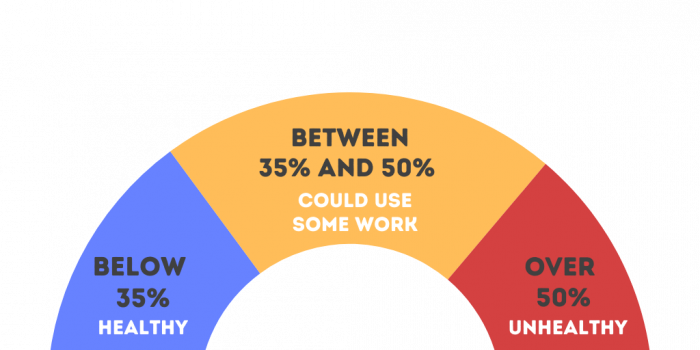
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Debt-to-Income Ratios
What’s a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio for a Business?
A good debt-to-income ratio varies by industry, but generally, a ratio below 35% is considered healthy. This indicates that your business has enough income to cover its debts comfortably, leaving room for growth and unexpected expenses. Ratios above 36% may signal that your business is carrying too much debt relative to its income, which can strain cash flow and limit your ability to invest in new opportunities.
Signs Your Debt-to-Income Ratio Might Be Too High
If your debt-to-income ratio is creeping upward, there are several warning signs to watch for. You might find that more of your revenue is going toward debt repayment, leaving less available for other expenses. You may also struggle to obtain new financing or find that lenders are offering less favorable terms. Additionally, high ratios can lead to increased stress on your business’s cash flow, making it difficult to manage day-to-day operations.
Consequences of an Unhealthy Debt-to-Income Ratio
An unhealthy debt-to-income ratio can have far-reaching consequences for your business. It can limit your access to credit, increase borrowing costs, and strain your relationships with creditors. Over time, a high ratio can erode your business’s financial stability, leading to cash flow problems, missed payments, and even insolvency. Addressing an unhealthy ratio is crucial to preserving your business’s long-term viability.
Strategies for Managing Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Reducing Debt: Practical Steps for Business Owners
Reducing debt is one of the most effective ways to improve your debt-to-income ratio. Start by prioritizing high-interest debt, as this will free up more income for other uses. Consider negotiating with creditors for better terms or consolidating debt to reduce your overall payments. Additionally, avoid taking on new debt unless it’s absolutely necessary and strategically beneficial.
Increasing Income: Boosting Revenue to Balance the Ratio
Increasing your income is the other side of the equation. Look for ways to boost sales, whether through marketing efforts, expanding your product line, or improving customer retention. Additionally, consider raising prices if your market can bear it. Every dollar of additional income helps to lower your debt-to-income ratio, giving your business more financial breathing room.
Refinancing Options: When and How to Refinance Business Debt
Refinancing can be a smart move if it allows you to secure a lower interest rate or more favorable terms. This can reduce your monthly payments and lower your debt-to-income ratio. However, it’s important to weigh the costs and benefits carefully. Refinancing should be done strategically, with an eye toward improving your overall financial position.
Negotiating with Creditors: Tips for Reducing Debt
If your debt-to-income ratio is uncomfortably high, negotiating with creditors may be necessary. Many creditors are willing to work with businesses to restructure debt, whether through extended payment terms, lower interest rates, or even debt forgiveness in some cases. Approaching creditors proactively, with a clear plan for repayment, can increase your chances of securing better terms.
How to Improve Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Cutting Unnecessary Expenses to Lower Debt
One of the simplest ways to improve your debt-to-income ratio is to cut unnecessary expenses. Review your budget to identify areas where you can reduce costs, whether through renegotiating contracts, eliminating non-essential spending, or finding more cost-effective suppliers. Every dollar saved can be applied to debt reduction, helping to bring your ratio into a healthier range.
Streamlining Operations to Increase Profit Margins
Streamlining operations can also boost your income, improving your debt-to-income ratio. Look for inefficiencies in your processes and explore ways to do more with less. This might involve adopting new technologies, automating tasks, or reorganizing your workforce to better align with your business’s needs. By increasing your profit margins, you can generate more income to cover your debts.
Strategic Borrowing: When Taking on New Debt Makes Sense
While reducing debt is important, there are times when taking on new debt can actually improve your debt-to-income ratio in the long run. Strategic borrowing for investments that increase your income—such as new equipment, expansion into new markets, or hiring key personnel—can pay off if managed carefully. The key is to ensure that the expected returns outweigh the cost of the debt.
Utilizing Financial Advisors to Balance Your Ratio
Navigating the complexities of debt management can be challenging, and this is where financial advisors come in. A qualified advisor can help you analyze your debt-to-income ratio, identify opportunities for improvement, and develop a plan for achieving financial balance. Their expertise can be invaluable in guiding your business toward a healthier financial future.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Overborrowing: When Debt Becomes a Burden
One of the most common mistakes businesses make is overborrowing. While debt can be a useful tool, taking on too much can quickly turn it into a burden. Overborrowing can lead to a high debt-to-income ratio, straining your cash flow and limiting your ability to invest in growth. It’s important to borrow strategically and avoid taking on more debt than your business can comfortably manage.
Ignoring Income Opportunities: The Pitfalls of Stagnant Revenue
Another common mistake is ignoring opportunities to increase income. Stagnant revenue can lead to a worsening debt-to-income ratio, especially if your debt continues to grow. Businesses should always be on the lookout for new ways to generate revenue, whether through expanding their product line, entering new markets, or enhancing their marketing efforts.
Misinterpreting Debt-to-Income Ratios: Common Misconceptions
Finally, it’s important to avoid misinterpreting your debt-to-income ratio. Some businesses mistakenly believe that a high ratio is always bad, while others may underestimate the risks of a low ratio. The truth is that the right ratio depends on your industry, business model, and financial goals. Understanding the nuances of your ratio can help you make more informed decisions.
Tools and Resources
Financial Tools for Monitoring Debt-to-Income Ratios
There are numerous tools available to help businesses monitor their debt-to-income ratios. From accounting software to specialized financial calculators, these tools can provide valuable insights into your financial health. Regularly tracking your ratio allows you to spot trends and make adjustments before problems arise.
Best Practices for Regularly Reviewing Your Ratios
Regularly reviewing your debt-to-income ratio is a best practice for maintaining financial health. Set aside time each month or quarter to analyze your ratio, review your financial statements, and make any necessary adjustments. This proactive approach can help you stay on top of your finances and avoid unpleasant surprises.
Hiring Financial Experts: When to Get Professional Help
If managing your debt-to-income ratio feels overwhelming, it may be time to seek professional help. Financial experts can provide guidance on everything from debt management to income generation, helping you achieve a healthier ratio. Whether you need a one-time consultation or ongoing support, hiring a financial advisor can be a worthwhile investment in your business’s future.
Real-World Examples
Case Studies: Successful Businesses with Healthy Ratios
Learning from others can provide valuable insights into how to manage your debt-to-income ratio effectively. Consider the example of a small manufacturing business that maintained a low ratio by carefully managing its debt and investing in revenue-generating activities. By keeping its ratio below 30%, the business was able to secure favorable financing and expand its operations without overextending itself.
Lessons from Businesses that Struggled with Debt-to-Income Ratios
On the flip side, there are lessons to be learned from businesses that struggled with high debt-to-income ratios. Take, for instance, a retail company that took on too much debt during an expansion phase. When sales didn’t meet expectations, the company found itself unable to cover its debt payments, leading to layoffs and store closures. This cautionary tale highlights the importance of careful planning and realistic projections when managing debt.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy debt-to-income ratio is crucial for the long-term success and financial stability of your business. By understanding this key metric and actively managing both your debt and income, you can position your business for growth, secure favorable financing, and avoid the pitfalls of overleveraging.
Regularly reviewing your ratio, making informed financial decisions, and seeking professional advice when needed will help keep your business on a solid financial footing, ensuring that it not only survives but thrives in a competitive landscape.

